PTFE Heat Shrinkable Tubing (PTFE Heat Shrinkable Tubing) is widely used in a variety of industries such as electrical, automotive, aerospace and others due to its excellent high temperature resistance, chemical inertness and electrical insulation properties. Choosing the right size of PTFE heat shrinkable tubing is critical to ensuring its performance in real-world applications.
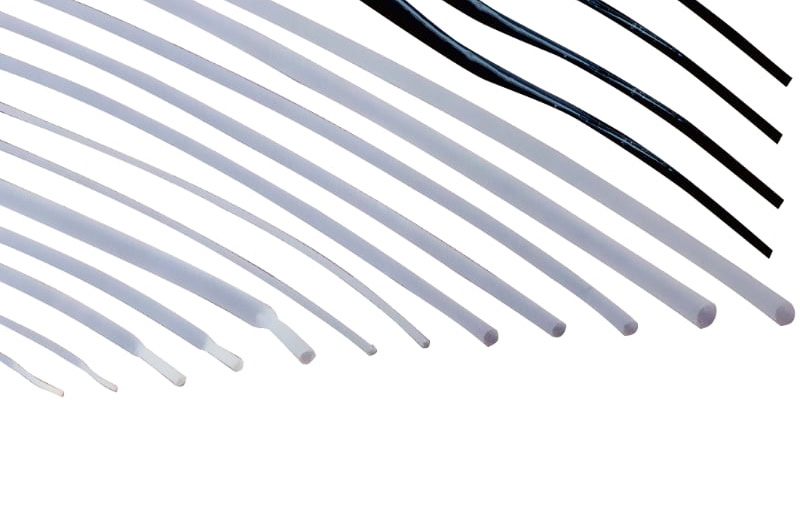

1. Understanding the Basic Shrinkage Principle of PTFE Heat Shrink Tubing
One of the main characteristics of PTFE heat shrink tubing is its heat shrinkability. When heated by a heat source (such as a heat gun or industrial oven), PTFE heat shrink tubing shrinks to a certain percentage of its original diameter, which is its shrinkage ratio. Common PTFE heat shrink tubing shrinkage ratios are 2:1 and 4:1, indicating that the diameter can be reduced to half or a quarter of its initial size, respectively. For example, a Heat Shrinkable Tube with an initial diameter of 10mm and a shrinkage ratio of 2:1 can shrink to a diameter of 5mm after heating.
2. Selecting the right size heat shrink tubing for the diameter of the cable or pipe
The key to selecting PTFE heat shrink tubing is to choose the right initial diameter and shrinkage diameter. When choosing, you need to make sure that the initial diameter of the heat shrink tubing is large enough to fit smoothly over the cable, pipe or other object being protected. It is also necessary to ensure that the post-shrink diameter is large enough to wrap tightly around the object to provide effective protection and insulation.
Step 1: Measure the Diameter of the Cable or Pipe
Before selecting PTFE heat shrink tubing, you need to accurately measure the outside diameter of the cable, pipe or other covered object. Make sure the measurement is accurate to avoid choosing an unsuitable size due to errors.
Step 2: Select Initial Diameter of Heat Shrink Tubing
It is generally recommended that the initial diameter of the heat shrink tubing be at least 20% to 30% larger than the maximum diameter of the cable or pipe. This ensures that the heat shrink tubing will slide onto the surface of the cable or pipe when it is not heated and will not be too small for installation. For example, if the cable is 10mm in diameter, it is recommended to choose PTFE heat shrink tubing with a diameter of 12mm to 14mm. If larger joint or node sections need to be covered, the maximum diameter of these sections should also be taken into account.
Step 3: Confirm Shrink Diameter
When selecting heat shrink tubing, the post-shrink diameter also needs to be considered. The post-shrink diameter should be slightly smaller than the outer diameter of the cable or pipe to ensure that the heat shrink tubing is able to wrap tightly around the cable after shrinking to form a strong protective layer.
For example, if the diameter of the cable is 10mm, it is recommended to choose a Heat Shrinkable Tube with a post-shrinkage diameter of less than 10mm. For heat shrink tubing with a 2:1 shrink ratio, an initial diameter of 14mm will shrink to a diameter of 7mm when heated to completely cover the cable and form a tight fit.
3. Consider the shrinkage ratio
Different shrinkage ratios determine the flexibility of heat shrink tubing. Common shrink ratios are 2:1 and 4:1, which means that the heat shrink tubing can be reduced to 1/2 or 1/4 of its initial diameter, respectively. choosing the right shrink ratio takes into account the ease of installation and the tightness of the wrap.
2:1 Shrinkage Ratio: Suitable for use on objects with small or no significant change in size. It is easier to install and widely used for most standard insulation needs.
4:1 Shrinkage Ratio: Suitable for use on objects with large dimensional variations, or where joints and irregular shapes need to be covered. It is more flexible and can be adapted to more complex applications.
Example:
If the diameter of the pipe does not vary much and there are no visible jointed parts, heat shrinkable tubing with a 2:1 shrinkage ratio is sufficient.
If the surface of the object to be covered has a large diameter variation, such as a joint section much larger than the diameter of the cable, a 4:1 shrink ratio ensures that the shrinkage remains tight when covering the larger section.
4. Consider wall thickness
In addition to diameter and shrinkage ratio, wall thickness is also an important factor in the selection of PTFE heat shrink tubing. Wall thickness directly affects the insulating properties, abrasion resistance and mechanical strength of the tubing. Generally, the greater the wall thickness, the greater the protective properties of the heat shrink tubing. However, it should be noted that too thick a wall thickness may increase the heat shrink time, affecting flexibility and installation difficulty.
For insulation protection of electronic equipment or cables, thinner PTFE heat shrink tubing will suffice.
For applications requiring additional mechanical protection or exposure to harsh environments, a thicker wall thickness is more appropriate.
5. Application Scenarios for PTFE Heat Shrink Tubing
In practice, PTFE heat shrink tubing is commonly used in the following scenarios:
Electrical insulation: suitable for high-voltage cables, motor coil insulation protection.
Chemical protection: Used in chemical processing equipment for the protection of pipes and cables to prevent chemical erosion.
High-temperature protection: For use in high-temperature environments such as aerospace and automotive engines to ensure the safe operation of equipment.
Mechanical protection: protects cables and pipes from mechanical abrasion and prolongs service life.
Choosing the right size of PTFE heat shrink tubing is not complicated, it is simply a matter of choosing based on the diameter of the object, the shrinkage ratio, and the desired wall thickness. Ensure that the initial diameter is greater than the maximum diameter of the protected object, while the heat-shrinkable diameter is smaller than the minimum diameter of the protected object to ensure a tight fit. In addition, select the appropriate shrinkage ratio and wall thickness to meet the needs of the particular application. Proper selection of PTFE heat shrink tubing will greatly enhance its protective performance and service life, providing the best possible protection for your equipment.



 English
English

